Inquiries about this product
Toyotsu Chemiplas Corporation
Functional Materials Group
TEL:03-4306-8665
[sanyo]
It is a lineup of functional additives of Sanyo Chemical Industries.
We deals with characteristic additives such as hydrophilic agent,
resin modifiers, permanent antistatic agents, polyethylene glycol, etc.
We prepare sample application that quantity limited for development.
Please contact our sales office for an order.
Make sure to read “Safety Data Sheet” (SDS) before use.
Please note that users are responsible for assuring suitability
and safety in their application of use.
Sanyo Chemical’s Products & Technologies Site
https://sanyo-chemical-solutions.com/
Download PDF
| Products name | Generic name | Action |
|---|---|---|
|
Hydrophilic agent, |
Adhesion improvement,Improvement of water wettability,Improvement of paintability,Adhesion improvement |
Compatibilizer UMEX
Umex is acid-modified polypropylene and improves dispersibility of pigments and fillers in polyolefin because of its high degree of modification and the low melt viscosity.

<Features>
- Filler dispersibility in polyolefin with low dosage.
- Improvement in Molding Processability.
- Heat resistance equivalent to polypropylene.
<Applications>
Glass fiber Dispersibility


Wood flour Dispersibility

UMEX Grades
| Grades | Appearance | Melting point (℃) |
Melt viscosity (160℃) (mPa・s) |
Acid value (mgKOH/g) |
Molecular weight | Features |
| UMEX 1001 | Yellow granule | 142 | 15,000 | 26 | 45,000 | Standard |
| UMEX 1010 | Yellow granule | 135 | 6,000 | 52 | 30,000 | |
| UMEX 100TS | Pale yellow powder | 136 | 120 | 3.5 | 9,000 | |
| UMEX 5200 | Yellow granule | 124 | 20,000 | 11 | 70,000 | Low melting point |
Melting point : DSC method, Acid value : ASTM D1386
Molecular weight : Gel permeation chromatography (GPC) using polystyrene standards.
UMEX products are a series of maleic-acid modified
low-molecular weight polyolefins. These products have
very high acid values,resulting in outstanding effectiveness
at low dosage.
Structure of UMEX
Polypropylene Segment
- Compatibility with polyolefin
Maleic anhydride Part
- Reactivity
- Dispersibility of fillers and pigments
- Adhesion properties
UMEX can be dry blended along with filler, pigment and resin.
Properties of UMEX products
Properties of UMEX products
Exp. 1 Glass Fiber Dispersion for Polypropylene
Addition of a small percentage of
UMEX (0.5-5wt%) results in a
increase in flexural strength and
other physical properties of glass
fiber reinforced plastic (GFRP).
■ UMEX 1001 added
■ Competing grade added(High Mw, low acid value type)
| Mechanical properties | UMEX 1001(1wt% added) | Competing grade(1wt% added) | Blank |
| Flexural strength (MPa) | 120 | 80 | 50 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 72 | 70 | 27 |
| Izot impact strength-notched (kJ/m2) | 11 | 8 | 9 |
Materials
Polypropylene(70wt%), glass fiber* (30wt%) and UMEX were kneaded using a twin screw extruder at
220℃ andthen injection molded. (Nozzle temperature : 220℃, Mold temperature : 50℃)
*Glass fiber : Chopped strand (Fiber length = 3mm, Fiber diameter = 13μm)
Test methods
Flexural test : ASTM D790, Tensile test : ASTM D638, Izot impact strength : ASTM D256
Exp. 1 Glass Fiber Dispersion for Polypropylene
(Glass Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene)
SEM images of the fractured cross section after izod testing.
Adhesion of glass fiber to polypropylene is improved.
Exp. 2 Carbon Fiber Dispersion for Polypropylene
(Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene)
Addition of a small percentage of UMEX
(1-2wt%)results in a increase in flexural
strength and other physical properties of
carbon fiber reinforced thermal plastic
(CFRTP).
■ UMEX 1001 added
■ Competing grade* added
| Mechanical properties | UMEX 10011wt% added | Competing grade* 1wt% added | Control |
| Flexural strength (MPa) | 135 | 64 | 84 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 97 | 57 | 43 |
| Deflection temperature under load (℃) | 145 | 136 | 115 |
Materials
Polypropylene(70wt%), carbon fiber**(30wt%) and UMEX were kneaded using a twin screw extruder at 250℃ and then injection molded. (Nozzle temperature : 250℃, Mold temperature : 50℃)
*Competing grade : High Mw, low acid value type
**Carbon fiber : PAN type chopped fiber (Fiber length = 6mm)
Test methods
Flexural test : ASTM D790, Tensile test : ASTM D638, Deflection temperature under load : ASTM D648(1.8MPa)
Exp. 2 Carbon Fiber Dispersion for Polypropylene
(Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene)
SEM images of the fractured cross section after izod testing.
UMEX can help disperse carbon fiber into the base polypropylene.
Exp. 3 Wood Flour Dispersion for Polypropylene
(Wood Plastic Composites Based on Polypropylene)
Addition of a small percentage of UMEX
(0.5-2wt%) results in a increase in
flexural strength and other physical
properties of wood plastic composites
(WPC).
■ UMEX 1010 added
■ Competing grade* added Materials
| Mechanical properties | UMEX 1010 1wt% added | Competing grade* 1wt% added | Control |
| Flexural strength (MPa) | 71 | 61 | 49 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 47 | 38 | 38 |
| Tensile modulus (MPa) | 550 | 540 | 470 |
Materials
Wood flour** (50wt%), polypropylene(50wt%) and UMEX were kneaded using a twin screw extruder at 200℃ and then injection molded. (Nozzle temperature: 200 ℃, Mold temperature: 50 ℃)
*Competing grade : High Mw, low acid value type
**Wood flour : 180μm pass, dried at 80℃ for 2hours.
Test methods
Flexural test : ASTM D790, Tensile test : ASTM D638
Exp. 3 Wood Flour Dispersion for Polypropylene
(Wood Plastic Composites Based on Polypropylene)
SEM images of the cross section.
UMEX can help disperse cellulose fibers into the base polypropylene.
Effect on heat loss properties in N2 gas
Test method
Heat rate : 10℃/min Ambience : N2
Effect on MFR
Materials
UMEX and polypropylene* were kneaded using a twin screw extruder at 220℃.
*Polypropylene : MFR = 11, block PP
Test method
MFR : Measured at 230℃, 2.16kgf.
Resin Compatibility
| Resin | Compatibility |
| LDPE | ○ |
| HDPE | ○ |
| PP | ○ |
| EVA | △ |
| PVC | × |
| PS | × |
| 6Ny | ○ |
| PC | △ |
| PBT | △ |
| m-PPE | × |
| PMMA | △ |
| ABS | △ |
UMEX / Resin = 5 / 95
○ ・・・ △ ・・・ ×
Compatible Incompatible
Solvent Resistance
| Solvent | Room temperature | Boiling point |
| Toluene | I | S |
| Xylene | I | S |
| n-Hexane | I | I |
| n-Heptane | I | I |
| Ethyl acetate | I | I |
| Butyl acetate | I | I |
| Methyl ethyl ketone | I | I |
| Methyl isobutyl ketone | I | I |
| ethanol | I | I |
| Isopropanol | I | I |
UMEX / Solvent = 1 / 4 ( wt / wt )
S : Soluble , I : Insoluble
Permanent Antistatic Additives
PELESTAT/PELECTRON
PELECTRON/PELESTATimpart permanent antistatic properties to resins such as ABS, PP, and PE.

<Features>
- Due to it’s good dispersivility to base resins, it doesn’t affect physical properties and moldability of base resins.
- Humidity independence.
- Superior Cleanness (Non bleeding out type).
- Can lower surface resistivity to 10^8-10^9 [Ω/sq.] level.(in case of PELECTRON)
PELESTAT Standard grades
| No.1 PELESTAT 300 |
No.2 PELESTAT 230 |
No.3 PELESTAT NC6321 |
No.4 PELESTAT NC7530 |
|
| Basic structure | PP-b-PEO | PP-b-PEO | 6Ny-b-PEO | 6Ny-b-PEO |
| Melting point (℃) | 135 | 163 | 203 | 176 |
| MFR (g/10min) | 30 (190℃,21.18N) |
14 (190℃,21.18N) |
20 (215℃,21.18N) |
10 (190℃,21.18N) |
| Refractive index | 1.49 | 1.49 | 1.51 | 1.53 |
| Surface resistivity *1(Ω/sq.) | 1×108 | 5×107 | 1×109 | 2×109 |
| Recommended Molding method | Injection | Extrusion | Injection Extrusion |
Injection Extrusion |
| Adapted Thermoplastic resins | PP, PE etc. | PP, PE HIPS etc. | ABS, PC/ABS, PBT etc. | transparent-ABS, MS etc. |
| Features | - | - | - | High refractive index |
*1 : 23℃(73°F), 50% R.H.
PELECTRON Standard grades
| No.1 PELECTRON PVL |
No.2 PELECTRON AS |
|
| Basic structure | PP-b-PEO | PA6-b-PEO |
| Melting point (℃) | 135 | 195 |
| MFR (g/10min) | 15 (190℃, 21.18 N) |
30 (215℃, 21.18 N) |
| Refractive index | 1.49 | 1.50 |
| Surface resistivity *1(Ω/sq.) | 3×106 | 4×106 |
| Recommended Molding method | Injection Extrusion |
Injection Extrusion |
| Adapted Thermoplastic resins | PP, PE HIPS etc. | ABS, PC/ABS, PC etc. |
| Features | Low resistivity | Low resistivity |
*1 : 23℃(73°F), 50% R.H.
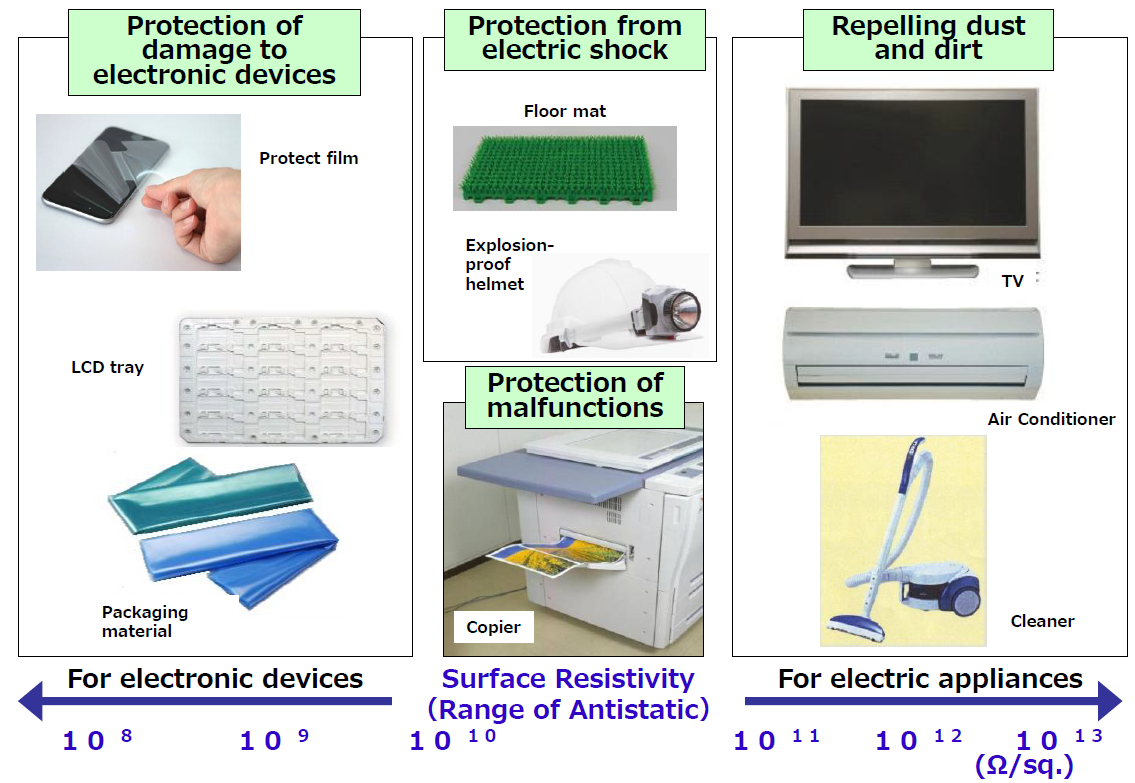
Purpose to Prevent Static Charge
Application
■Repelling dust and dirt
( Surface Resistivity :1012 (Ω/sq.) )
< For electric appliances, automobile interior component >
Dust box of cleaner
Base resin :transparent-ABS
(Injection molding)

Components of air conditioners
Base resin :HIPS
(Injection molding)

■Protection from electric shock
( Surface Resistivity :1010~1011 (Ω/sq.) )
<For explosion-proof products>
Explosion-proof helmet
Base resin :PP(Injection molding)

Flexible container (Inner bag )
Base resin :PE(blow molding)

Explosion-proof flashlight
Base resin :PA(Injection molding)

■Protection of damage to electronic devices
( Surface Resistivity :108~109 (Ω/sq.) )
<For electronic parts package>
Tray for IC chips , precision parts Base resin :
ABS, PP, m-PPE
(Injection molding)

Package for electronic parts, precision parts
Base resin :PE(blow molding)

LCD tray Base resin :PP
(extrusion molding→vaccum molding)

Antistatic Effect
Repelling dust and dirt because of low surface resistivity
Basic Structure of PELECTRON/PELESTAT
Morphology
Processing Flowchart
Normal molding method (Injection, Extrusion, etc.)
Surface Resistivity performance
<Example of the application to LDPE extruded film>
Effects on Physical Properties of Resin
| Item | Measuring method | LDPE/PELECTRON PVL=90/10 | LDPE |
| Surface Resistivity1) Ω/sq. | ASTM D 257 | 1×1011 | >1016 |
| MFR(190℃, 21.18N) g/10min | ASTM D 1238 | 3 | 2 |
| Tensile strength MPa | ASTM D 638 | 21 | 20 |
| Tensile strength at break % | ASTM D638 | 590 | 580 |
| Haze % | JIS K 7105 | 35 | 34 |
| Total light transmittance % | JIS K 7105 | 86 | 86 |
1) 23℃(73°F), 50% R.H.
Testing Methods
PELECTRON PVL and LDPE were dry-blended and molded using sheeting
equipment[extruder (20 mmØ, L/D=25, revolution rate: 50 rpm),
die (120 mm, die temp.: approx. 200oC( 392oF)] into sheets 100 μm
(approx. 3.9 mils).
Comparison data to
Low-Molecular-Weight Antistatic Additives
| PELESTAT ・PELECTRON | Low-Molecular-Weight Antistatic Additives | |
| Surface Resistivity(Ω/sq.) | 108~1012 | 109~1012 |
| Dosage (wt%) | 5~25 | 0.2~2 |
| Antistatic Sustainability | ○ | × |
| Humidity Independence | ○ | × |
| Antistatic at Directly after molding | ○ | × |
Comparison to Low-Molecular-Weight Antistatic Additives
Antistatic Substantivity
Number of washing [times]
Testing Methods
Surface of the test pieces was wiped with a water-soaked cotton cloth.
The test pieces were dried in a vacuum (130 Pa) at 70oC for 2 hours
and kept at 23oC, 50 % R.H. for 24 hours. Surface resistivity was
measured by using megohmmeter.
Humidity Independence
Relative Humidity [%] (Temp.:23℃)
Testing Methods
The test pieces kept at 23oC (73oF) under predetermined
humidity for 24 hours. The surface resistivity was measured by
using a megohmmeter.
Application
| Products name | Composition | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
|
Polyethylene glycol |
Number average molecular weight: 200 (calculated from hydroxyl value) |
|
|
Polyethylene glycol |
Number average molecular weight: 300 (calculated from hydroxyl value) |
|
|
Polyethylene glycol |
Number average molecular weight: 400 (calculated from hydroxyl value) |
|
|
Polyethylene glycol |
Number average molecular weight: 600 (calculated from hydroxyl value) |
|
|
Polyethylene glycol |
Number average molecular weight: 1000 (calculated from hydroxyl value) |
|
|
Polyethylene glycol |
Number average molecular weight: 550 (calculated from hydroxyl value) |
|
|
Polyethylene glycol |
Number average molecular weight: 1450 (calculated from hydroxyl value) |
|
|
Polyethylene glycol |
Number average molecular weight: 2000 (calculated from hydroxyl value) |
|
|
Polyethylene glycol |
Number average molecular weight: 3100 (calculated from hydroxyl value) |
|
|
Polyethylene glycol |
Number average molecular weight: 3400 (calculated from hydroxyl value) |
|
|
Polyethylene glycol |
Number average molecular weight: 8300 (calculated from hydroxyl value) |
|
|
Polyethylene glycol |
Number average molecular weight: 8300 (calculated from hydroxyl value) |
|
|
Polyethylene glycol |
Number average molecular weight: 11000 (calculated from hydroxyl value) |
|
|
Polyethylene glycol |
Number average molecular weight: 13000 (calculated from hydroxyl value) |
|
|
Polyethylene glycol |
Number average molecular weight: 20000 (calculated from hydroxyl value) |
|
|
Polyethylene glycol |
Number average molecular weight: 20000 (calculated from hydroxyl value) |
 SANYO CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES CO.,LTD.
SANYO CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES CO.,LTD.